Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), return the minimum difference between the values of any two different nodes in the tree.
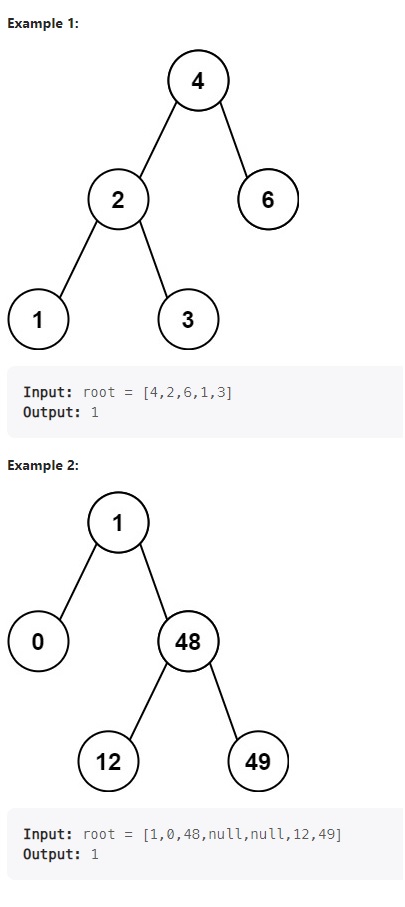
Example 1:
Input: root = [4,2,6,1,3]
Output: 1Example 2:
Input: root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49]
Output: 1Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 100].
0 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Minimum Distance Between BST Nodes (Recursive Depth First Search + In-Order Traversal Algorithm)
We can perform a Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm (DFS) in the order of in-order traversal manner on a Binary Search Tree (BST) which will give us a sorted array (list). And then, we can just compare the neighbour two elements to get the minimum difference. We can store all the elements in the list.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def minDiffInBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: def dfs(root): if not root: return [] return dfs(root.left) + [root.val] + dfs(root.right) nums = dfs(root) ans = inf for i in range(len(nums) - 1): ans = min(ans, abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1])) return ans |
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDiffInBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return []
return dfs(root.left) + [root.val] + dfs(root.right)
nums = dfs(root)
ans = inf
for i in range(len(nums) - 1):
ans = min(ans, abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]))
return ansAlternatively, we can use the generator and yield each element along the inorder traversal. We can also use the min function to get the min of all elements in the given iterables, and specify a default value if it is empty.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def minDiffInBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: def dfs(root): if not root: return yield from dfs(root.left) yield root.val yield from dfs(root.right) nums = list(dfs(root)) return min((abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]) for i in range(len(nums) - 1)), default=0) |
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDiffInBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return
yield from dfs(root.left)
yield root.val
yield from dfs(root.right)
nums = list(dfs(root))
return min((abs(nums[i] - nums[i + 1]) for i in range(len(nums) - 1)), default=0)Both these two approaches have O(N) time and O(N) space complexity. As we need to store N elements in the binary search tree (BST). Also, in general, a Recursion requires O(H) space usage.
However, we just need a previous value in the sorted list in order to compute the min difference. Thus, in Inorder traversal (where the time complexity is still O(N) as we need to traverse all nodes in the tree), we record the previous node if there is any. This method doesn’t require storing all elements in a separate list/array, but still, O(H) Recursion space complexity, and in the worst case, O(H)=O(N) when the given binary search tree is degraded e.g. only max 1 child node for every node in the binary search tree.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def minDiffInBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int: self.ans = inf self.prev = None def dfs(root): if not root: return dfs(root.left) if self.prev: self.ans = min(self.ans, abs(self.prev.val - root.val)) self.prev = root dfs(root.right) dfs(root) return self.ans |
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDiffInBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.ans = inf
self.prev = None
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return
dfs(root.left)
if self.prev:
self.ans = min(self.ans, abs(self.prev.val - root.val))
self.prev = root
dfs(root.right)
dfs(root)
return self.ansThe in-order traversal can be implemented via Recursion, also can be implemented via Stack approach, which is iterative.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: How can i make money using Crypto?
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal (via Breadth First Search Algorithm)