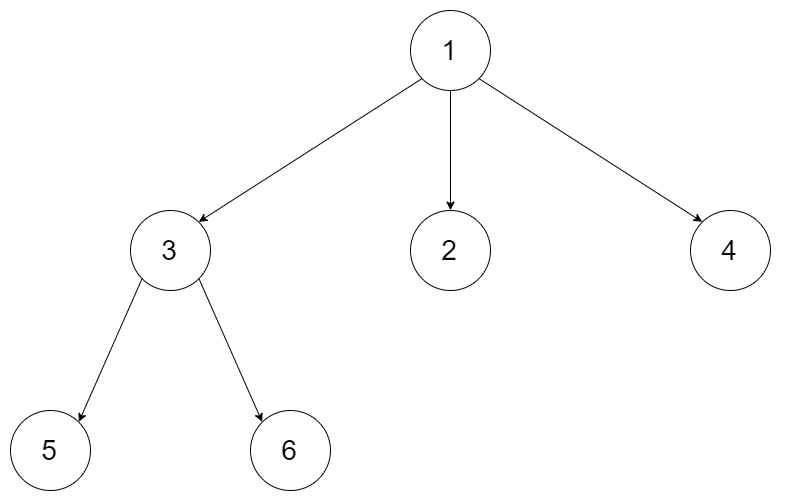
Given a n-ary tree, find its maximum depth. The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. For example, given a 3-ary tree:
We should return its max depth, which is 3. Note: The depth of the tree is at most 1000. The total number of nodes is at most 5000.
Definition of N-ary Tree in C++
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; vector<Node*> children; Node() {} Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; |
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};DFS (Depth First Search)
DFS is usually easy to implement using recursion. The depth of N-ary tree is the maximum depth of its subtree (children) plus one.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | class Solution { public: int maxDepth(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) { return 0; } int depth = 0; for (const auto &subTree: root->children) { auto d = maxDepth(subTree); depth = max(depth, d); } return depth + 1; // children depth plus one } }; |
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
for (const auto &subTree: root->children) {
auto d = maxDepth(subTree);
depth = max(depth, d);
}
return depth + 1; // children depth plus one
}
};BFS (Breadth First Search)
BFS travels the tree level by level. This is done by maintaining a queue and expanding the children nodes node by node. At each iteration, we also need to calculate its depth and push the depth together with the node in the queue.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | class Solution { public: int maxDepth(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; queue<pair<Node*, int>> Q; Q.push(make_pair(root, 1)); int depth = 1; while (Q.size() > 0) { auto p = Q.front(); Q.pop(); for (const auto &n: p.first->children) { Q.push(make_pair(n, p.second + 1)); // push children to queue depth = max(p.second + 1, depth); // record the maximum depth of current node } } return depth; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
queue<pair<Node*, int>> Q;
Q.push(make_pair(root, 1));
int depth = 1;
while (Q.size() > 0) {
auto p = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (const auto &n: p.first->children) {
Q.push(make_pair(n, p.second + 1)); // push children to queue
depth = max(p.second + 1, depth); // record the maximum depth of current node
}
}
return depth;
}
};Both BFS and DFS need to walk through the entire tree, and therefore, performance-wise, there is no much difference.
Compute the Maximum Depth for a N-ary Tree:
- Teaching Kids Programming – Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree via Depth First Search or Breadth First Search Algorithms
- Teaching Kids Programming – BFS Algorithm to Compute the Maximum Depth of the Binary Tree
- Teaching Kids Programming – Recursive Algorithm to Compute the Maximum Depth of the Binary Tree
- C++ Coding Exercise – Find Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: C++ Coding Exercise - Find Third Maximum in O(n)
Next Post: C++ Coding Exercise - Find Letter Case Permutation with DFS