Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
Given an integer array nums and an integer val, remove all occurrences of val in nums in-place. The relative order of the elements may be changed.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums. Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
Output: 2, nums = [2,2,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2
Output: 5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3,_,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 0, 1, 3, and 4.
Note that the five elements can be returned in any order.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).The problem statement clearly asks us to modify the array in-place and it also says that the element beyond the new length of the array can be anything. Given an element, we need to remove all the occurrences of it from the array. We don’t technically need to remove that element per-say, right?
We can move all the occurrences of this element to the end of the array. Use two pointers!Yet another direction of thought is to consider the elements to be removed as non-existent. In a single pass, if we keep copying the visible elements in-place, that should also solve this problem for us.
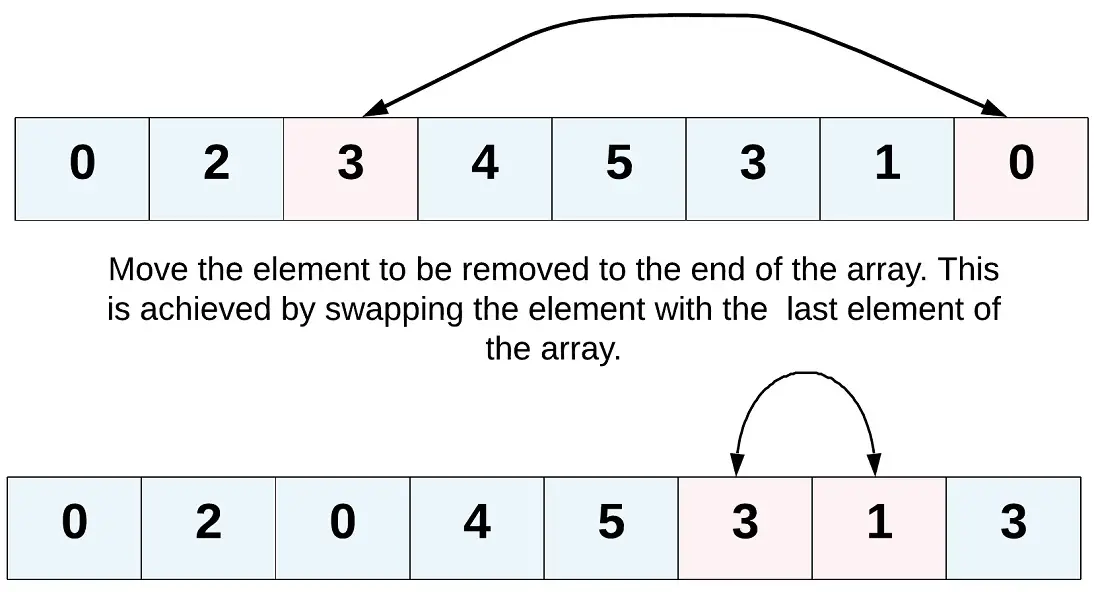
Two Pointer to Remove Elements
We can use two pointer algorithm to move the target (element to remove) with the elements at the end (Right Pointer).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | class Solution: def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int: j = len(nums) - 1 i = 0 while i <= j: if nums[i] == val: nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i] j -= 1 else: i += 1 return i |
class Solution:
def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
j = len(nums) - 1
i = 0
while i <= j:
if nums[i] == val:
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
j -= 1
else:
i += 1
return i Time complexity is O(N) and space complexity is O(1).
Using a Tail Pointer to Remove Element
We can also use a tail pointer to store the elements that we want to keep.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | class Solution: def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int: j = 0 for i in nums: if i != val: nums[j] = i j += 1 return j |
class Solution:
def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
j = 0
for i in nums:
if i != val:
nums[j] = i
j += 1
return j Time complexity is O(N) and the space complexity is O(1) constant.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Algorithm to Determine Three Divisors Numbers
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Pairwise Linked List Nodes Swap Algorithm