Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
We stack glasses in a pyramid, where the first row has 1 glass, the second row has 2 glasses, and so on until the 100th row. Each glass holds one cup of champagne.
Then, some champagne is poured into the first glass at the top. When the topmost glass is full, any excess liquid poured will fall equally to the glass immediately to the left and right of it. When those glasses become full, any excess champagne will fall equally to the left and right of those glasses, and so on. (A glass at the bottom row has its excess champagne fall on the floor.)
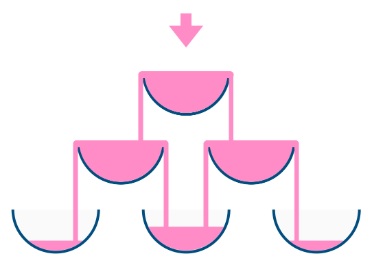
For example, after one cup of champagne is poured, the top most glass is full. After two cups of champagne are poured, the two glasses on the second row are half full. After three cups of champagne are poured, those two cups become full – there are 3 full glasses total now. After four cups of champagne are poured, the third row has the middle glass half full, and the two outside glasses are a quarter full, as pictured below.
Now after pouring some non-negative integer cups of champagne, return how full the jth glass in the ith row is (both i and j are 0-indexed.)
Example 1:
Input: poured = 1, query_row = 1, query_glass = 1
Output: 0.00000
Explanation: We poured 1 cup of champange to the top glass of the tower (which is indexed as (0, 0)). There will be no excess liquid so all the glasses under the top glass will remain empty.Example 2:
Input: poured = 2, query_row = 1, query_glass = 1
Output: 0.50000
Explanation: We poured 2 cups of champange to the top glass of the tower (which is indexed as (0, 0)). There is one cup of excess liquid. The glass indexed as (1, 0) and the glass indexed as (1, 1) will share the excess liquid equally, and each will get half cup of champange.Example 3:
Input: poured = 100000009, query_row = 33, query_glass = 17
Output: 1.00000Constraints:
0 <= poured <= 10^9
0 <= query_glass <= query_row < 100
Compute the Amount of Wine in a Champagne Tower: Top Down Dynamic Programming Algorithm – Recursion with Memoization
We can solve this Recursively with Memoization, aka the Top Down Dynamic Programming Algorithm.
For each glass, we need to figure out two things: the amount of liquid (water or wine, apple juice) that stays in the glass, and the amount that overflows. And each glass overflows in two directions evenly. Each glass takes 50% of the overflow in two glasses above. Similar to Pascal Triangle, we can solve this using Recursion with Memoization.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class Solution: def champagneTower(self, a: int, r: int, c: int) -> float: @cache def f(r, c): if c < 0 or c > r: return 0, 0 if r == 0: return max(a - 1, 0), min(a, 1) e1, _ = f(r - 1, c) e2, _ = f(r - 1, c - 1) total = (e1 + e2)*0.5 return max(total - 1, 0), min(total, 1) return f(r, c)[1] |
class Solution:
def champagneTower(self, a: int, r: int, c: int) -> float:
@cache
def f(r, c):
if c < 0 or c > r:
return 0, 0
if r == 0:
return max(a - 1, 0), min(a, 1)
e1, _ = f(r - 1, c)
e2, _ = f(r - 1, c - 1)
total = (e1 + e2)*0.5
return max(total - 1, 0), min(total, 1)
return f(r, c)[1]–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: How to Check the Balance of a Ethereum Wallet Address?
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Maximum Odd Binary Number