Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
Given a binary tree root, return the longest path consisting of even values between any two nodes in the tree.
Constraints
n ≤ 100,000 where n is the number of nodes in root
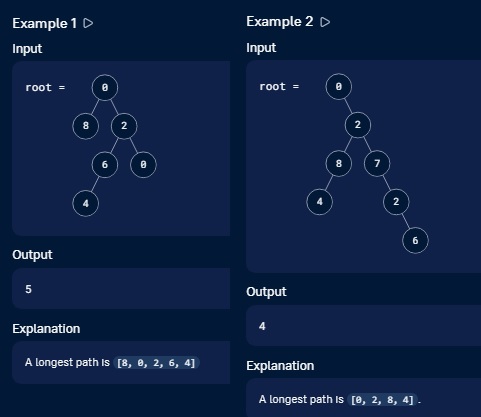
Example 1
Input
root = [0, [8, null, null], [2, [6, [4, null, null], null], [0, null, null]]]
Output
5
Explanation
A longest path is [8, 0, 2, 6, 4]Example 2
Input
root = [0, null, [2, [8, [4, null, null], null], [7, null, [2, null, [6, null, null]]]]]
Output
4
Explanation
A longest path is [0, 2, 8, 4].can the inorder traversal of tree help ?.
A similar approach to the Diameter of the tree?
Breadth First Search Algorithm to Compute the Longest Even Value Path in Binary Tree (Graph)
We can convert the binary tree into a Graph (and store the Graph in a adjacent list). Then for every even vertex in the Graph, we can perform a Breadth First Search algorithm to return the longest even node path from that node. And we can store the longest/maximum even path for the Graph.
To convert the binary tree into a Graph – we can do a Depth First Search or Breadth First Search. The following using DFS (Recursion) to convert the binary tree into a Graph (a collection of vertex and edges).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | # class Tree: # def __init__(self, val, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def solve(self, root): G = defaultdict(list) def dfs(root, p): if not root: return dfs(root.left, root) dfs(root.right, root) if p: G[root].append(p) G[p].append(root) def bfs(root): if not root or root.val & 1: return 0 ans = 0 q = deque([(root, 1)]) seen = set() seen.add(root) while q: cur, d = q.popleft() ans = max(ans, d) for c in G[cur]: if c.val & 1 == 0 and c not in seen: seen.add(c) q.append((c, d + 1)) return ans dfs(root, None) ans = 0 for i in G: if i.val & 1 == 0: ans = max(ans, bfs(i)) return ans |
# class Tree:
# def __init__(self, val, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def solve(self, root):
G = defaultdict(list)
def dfs(root, p):
if not root:
return
dfs(root.left, root)
dfs(root.right, root)
if p:
G[root].append(p)
G[p].append(root)
def bfs(root):
if not root or root.val & 1:
return 0
ans = 0
q = deque([(root, 1)])
seen = set()
seen.add(root)
while q:
cur, d = q.popleft()
ans = max(ans, d)
for c in G[cur]:
if c.val & 1 == 0 and c not in seen:
seen.add(c)
q.append((c, d + 1))
return ans
dfs(root, None)
ans = 0
for i in G:
if i.val & 1 == 0:
ans = max(ans, bfs(i))
return ansWe can also perform a Recursive Depth First Search algorithm on even vertex to obtain the longest even path from that node.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | # class Tree: # def __init__(self, val, left=None, right=None): # self.val = val # self.left = left # self.right = right class Solution: def solve(self, root): G = defaultdict(list) def dfs(root, p): if not root: return dfs(root.left, root) dfs(root.right, root) if p: G[root].append(p) G[p].append(root) def dfs2(root, seen = set()): if not root or root in seen or root.val & 1: return 0 seen.add(root) ans = 0 for n in G[root]: ans = max(ans, dfs2(n, seen) + 1) return ans dfs(root, None) ans = 0 for i in G: if i.val & 1 == 0: ans = max(ans, dfs2(i, set())) return ans |
# class Tree:
# def __init__(self, val, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def solve(self, root):
G = defaultdict(list)
def dfs(root, p):
if not root:
return
dfs(root.left, root)
dfs(root.right, root)
if p:
G[root].append(p)
G[p].append(root)
def dfs2(root, seen = set()):
if not root or root in seen or root.val & 1:
return 0
seen.add(root)
ans = 0
for n in G[root]:
ans = max(ans, dfs2(n, seen) + 1)
return ans
dfs(root, None)
ans = 0
for i in G:
if i.val & 1 == 0:
ans = max(ans, dfs2(i, set()))
return ansTime complexity is O(N^2) as we have N vertex and for each vertex, the BFS or DFS requires O(N) time e.g. considering a linked list Graph with all even nodes.
Obviously, using the Pure DFS is more efficient: Teaching Kids Programming – Longest Even Value Path in Binary Tree using Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
Longest Path Problems in Binary Tree
- Teaching Kids Programming – Longest Even Value Path in Binary Tree via Graph Breadth First Search Algorithm
- Teaching Kids Programming – Longest Even Value Path in Binary Tree using Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
- Teaching Kids Programming – Longest Path in Binary Tree via Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
- Teaching Kids Programming – Longest Path in Binary Tree via Diameter Algorithm (DFS + BFS)
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Longest Even Value Path in Binary Tree using Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
Next Post: Javascript Function to Convert Hex String to ASCII Characters (Hexadecimal)