Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same.
Since it is impossible to change the length of the array in some languages, you must instead have the result be placed in the first part of the array nums. More formally, if there are k elements after removing the duplicates, then the first k elements of nums should hold the final result. It does not matter what you leave beyond the first k elements.
Return k after placing the final result in the first k slots of nums.
Do not allocate extra space for another array. You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Custom Judge: The judge will test your solution with the following code:
int[] nums = [...]; // Input array int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation assert k == expectedNums.length; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i]; }If all assertions pass, then your solution will be accepted.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
Example 2:Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
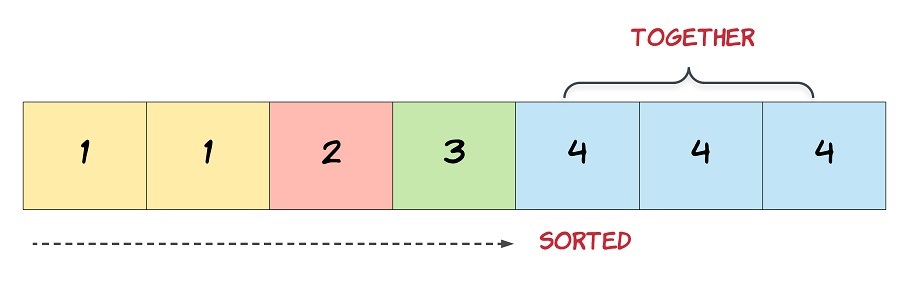
It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).In this problem, the key point to focus on is the input array being sorted. As far as duplicate elements are concerned, what is their positioning in the array when the given array is sorted? Look at the image above for the answer. If we know the position of one of the elements, do we also know the positioning of all the duplicate elements?
We need to modify the array in-place and the size of the final array would potentially be smaller than the size of the input array. So, we ought to use a two-pointer approach here. One, that would keep track of the current element in the original array and another one for just the unique elements.
Essentially, once an element is encountered, you simply need to bypass its duplicates and move on to the next unique element.
Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array using Set
If we can use an additonal space we can use a hash set to store only the unique numbers (each number inc. duplicates appears only once). Then we sort the numbers, and convert them to list. Finally we copy over to the original array/list.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | class Solution: def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: a = list(sorted(set(nums))) for i in range(len(a)): nums[i] = a[i] return len(a) |
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
a = list(sorted(set(nums)))
for i in range(len(a)):
nums[i] = a[i]
return len(a)The time complexity is O(NLogN) since we sort the numbers in a set (elements in a set do not have orders). The space complexity is O(N) as we are using a set.
Linear Algorithm Constant Space to Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array via Two Pointer Algorithm
We can use two pointers A and B (Two Pointer Algorithms). We go through each element in the list, which is indicated by pointer AThe first time a number appears in the sorted array (which can be checked by comparing equity with its previous number), we can assign it to the array at the pointer B and then we increment the B.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | class Solution: def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: a = 1 for i in range(1, len(nums)): if nums[i] != nums[i - 1]: nums[a] = nums[i] a += 1 return a |
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
a = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] != nums[i - 1]:
nums[a] = nums[i]
a += 1
return aThe time complexity is O(N) – linear, and the space complexity is O(1) constant.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Teaching Kisd Programming - Finding the Length of a Linked List (Recursion and Iterative Algorithm)
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - High Accuracy Multiplication Algorithm (Multiply Strings)