Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
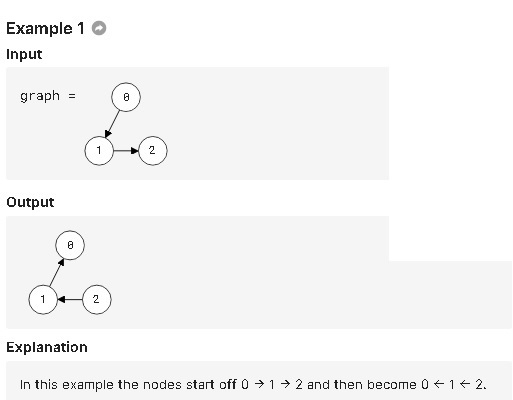
Given a directed graph represented as an adjacency list, return its reverse so if an edge goes from A to B, it now goes from B to A.
Each list in the adjacency list should be sorted in ascending order.
Constraints
0 ≤ n, m ≤ 250 where n is the number of rows and m is the maximum number of columns in graph
Algorithm to Reverse a Graph (Adjacency List)
A graph (noted as G(V, E) where V is set of vertices and E is set of edges) is a data structure that can be reprsented by Adjacency Matrix or Adjacency List. We can reverse a Graph by two steps. First, clone all the vertices and then iterate each edge in original Graph and add their reversed edges into the new Graph.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | class Solution: def reverseGraph(self, graph): # create the Graph with just vertices rev = [[] for _ in range(len(graph))] for u, v in enumerate(graph): for k in v: # iterate over each edge rev[k].append(u) # add reversed edge return rev |
class Solution:
def reverseGraph(self, graph):
# create the Graph with just vertices
rev = [[] for _ in range(len(graph))]
for u, v in enumerate(graph):
for k in v: # iterate over each edge
rev[k].append(u) # add reversed edge
return revThe time and space complexity is O(VE).
See also: Algorithms to Reverse a Graph (Adjacency List)
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Simple and Efficient C Program to Compute the Mathematic Constant E (Euler's number)
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Subtree with Maximum Value via Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm