We know the binary conversion, which is base two. The algorithm to convert to binary for a decimal integer, is to divide by two and concatenate the remainder in the reverse order. How about negative base – for example, base minus two – or negabinary?
Given any base r, we can rewrite every integer uniquely as follows:
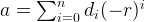
Why Negative Base?
One advantage of using negative base is that we don’t need a sign bit. For positive base like binary, a signed-integer which is 32 bit, however, the left-most bit (most significant bit) is used to represent the sign.
In negabinary, there is no sign bit. For example:
-15 = 110001 because (-2)^0 + (-2)^4 + (-2)^5 = 1 + 16 – 32.
Given a number N, return a string consisting of “0”s and “1”s that represents its value in base -2 (negative two). The returned string must have no leading zeroes, unless the string is “0”.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: “110”
Explantion: (-2) ^ 2 + (-2) ^ 1 = 2Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: “111”
Explantion: (-2) ^ 2 + (-2) ^ 1 + (-2) ^ 0 = 3Example 3:
Input: 4
Output: “100”
Explantion: (-2) ^ 2 = 40 <= N <= 10^9
How to Convert to Base -2 by Adjusting Remainder and Quotient?
The simplistic method is to adjust the remainder and quotient, as followed C++ implementation shows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | class Solution { public: string baseNeg2(int N) { string r = ""; while (N != 0) { int rem = N % (-2); N /= (-2); if (rem < 0) { rem += 2; // make remainder positive N ++; // adjust the quotient } r = std::to_string(rem) + r; } return r == "" ? "0" : r; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
string baseNeg2(int N) {
string r = "";
while (N != 0) {
int rem = N % (-2);
N /= (-2);
if (rem < 0) {
rem += 2; // make remainder positive
N ++; // adjust the quotient
}
r = std::to_string(rem) + r;
}
return r == "" ? "0" : r;
}
};For the proof and how it works, you might refer to the wiki: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Negative_base#Calculation
How to Convert to Base -2 by using Odd/Even rules?
As you might notice, for even bits, the values are the same as it were the positive base: (-2)^4 = (2)^4. When it comes to the odd bits, we might need to manually change the sign:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | class Solution { public: string baseNeg2(int N) { string r = ""; while (N != 0) { int rem = N % (-2); if (r.size() % 2 == 0) { N = (N - rem) / 2; } else { N = (N + rem) / 2; } r = std::to_string(rem) + r; } return r == "" ? "0" : r; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
string baseNeg2(int N) {
string r = "";
while (N != 0) {
int rem = N % (-2);
if (r.size() % 2 == 0) {
N = (N - rem) / 2;
} else {
N = (N + rem) / 2;
}
r = std::to_string(rem) + r;
}
return r == "" ? "0" : r;
}
};Both algorithms work at O(logN) time and space complexity – if we consider the string concatenation in C++ works O(1). You can always pre-allocate the string buffer or using StringBuilder in Java or C# to make it trivial.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Greedy Algorithm to Find the Largest Perimeter Triangle by Sorting
Next Post: Algorithms to Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In a String