A downside of K-Nearest Neighbors is that you need to hang on to your entire training dataset.
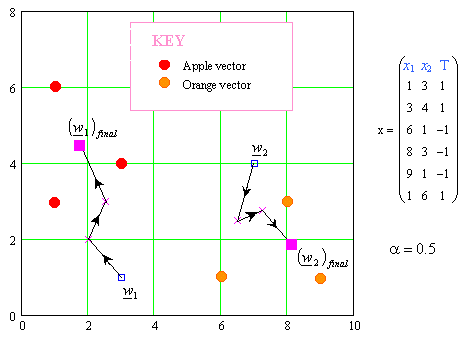
The Learning Vector Quantization algorithm (or LVQ for short) is an artificial neural network algorithm that allows you to choose how many training instances to hang onto and learns exactly what those instances should look like.
The representation for LVQ is a collection of codebook vectors. These are selected randomly in the beginning and adapted to best summarize the training dataset over a number of iterations of the learning algorithm.
After learned, the codebook vectors can be used to make predictions just like K-Nearest Neighbors. The most similar neighbor (best matching codebook vector) is found by calculating the distance between each codebook vector and the new data instance. The class value or (real value in the case of regression) for the best matching unit is then returned as the prediction.
Best results are achieved if you rescale your data to have the same range, such as between 0 and 1.
If you discover that KNN gives good results on your dataset try using LVQ to reduce the memory requirements of storing the entire training dataset.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: A Short Introduction to K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
Next Post: A Short Introduction: Support Vector Machines