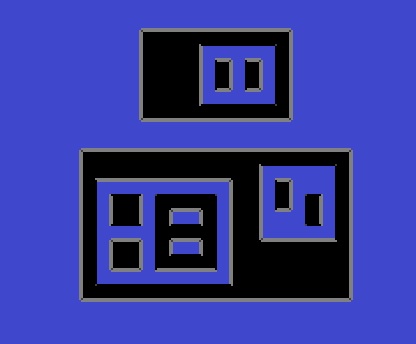
You are given a set of two-dimensional rectangular boxes on a two-dimensional Cartesian plane with the following assumptions and constraints:
- All boxes are axis-aligned, i.e. each box can be defined in terms of the Cartesian coordinates of its minimum corner {a, b} and its maximum corner {c, d} such that a < c and b < d.
- Boxes may be contained within other boxes or may be disjoint from one another, i.e. boxes do not overlap or touch one another.
- The boxes therefore partition the plane into a number of regions. The unbounded region, which lies outside of all the boxes, is classified as “sea”.
- All other regions are classified either as “sea” or as “land”, subject to the constraint that adjacent regions must not share the same classification.
The task is to read the definition of the rectangles from standard input formatted as defined below, and output the number of regions classified as “land” to standard output.
If you make any other assumptions as part of your solution then please make comments in the code. If there are further considerations that might affect the memory use or performance of your
solution then do make a note of them.
When submitting your solution please return all of your code, including any tests that you might have written and any documentation that you feel is appropriate. Please archive your solution
either as a .tar or .zip file.
Input Format
Some sample data is provided below for you to use when testing your solution. The first line contains an integer N denoting the number of boxes. The next N lines contain the four floating
point values a, b, c, d that define Cartesian coordinates of the minimum corner and maximum corner of each box separated by a single space.
N a1 b1 c1 d1 ... aN bN cN dN
Sample Input
14 1.0 1.0 10.0 6.0 1.5 1.5 6.0 5.0 2.0 2.0 3.0 3.0 2.0 3.5 3.0 4.5 3.5 2.0 5.5 4.5 4.0 3.5 5.0 4.0 4.0 2.5 5.0 3.0 7.0 3.0 9.5 5.5 7.5 4.0 8.0 5.0 8.5 3.5 9.0 4.5 3.0 7.0 8.0 10.0 5.0 7.5 7.5 9.5 5.5 8.0 6.0 9.0 6.5 8.0 7.0 9.0
Sample Output:
9
Breadth First Search Algorithm to Classify the Lands
We can first expand the first box into the queue with two possibilities, land or sea. Next, while the queue is not empty, we get the parent box and expand next box into the queue subject to the constraint – where adjacent boxes should not share same classification. We can pre-compute the adjacent relations between any two boxes. The tricky part here is to deal with the nested boxes where box A is inside box B and box B is inside box C – in this case, box A and box C is not adjacent.
TDD – Let’s write the Tests First
The following tests a few scenarios:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 | #include "stdafx.h" #include "CppUnitTest.h" #include "../LandAndSea/box.h" #include <vector> // https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19886397/how-to-solve-the-error-lnk2019-unresolved-external-symbol-function #include "../LandAndSea/landsolver.cpp" using namespace Microsoft::VisualStudio::CppUnitTestFramework; using namespace std; namespace LandAndSeaTests { TEST_CLASS(LandSolverTests) { public: // TestCase Given in the PDF TEST_METHOD(ExampleTestCases) { vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes; boxes.reserve(14); // prepare input boxes boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.0, 1.0, 10.0, 6.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.5, 1.5, 6.0, 5.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(2.0, 2.0, 3.0, 3.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(2.0, 3.5, 3.0, 4.5)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(3.5, 2.0, 5.5, 4.5)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(4.0, 3.5, 5.0, 4.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(4.0, 2.5, 5.0, 3.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(7.0, 3.0, 9.5, 5.5)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(7.5, 4.0, 8.0, 5.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(8.5, 3.5, 9.0, 4.5)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(3.0, 7.0, 8.0, 10.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 9.5)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(5.5, 8.0, 6.0, 9.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(6.5, 8.0, 7.0, 9.0)); // make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes Assert::AreEqual<int>(14, boxes.size()); // now it should ouput 9 Assert::AreEqual<int>(9, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands()); } // Two Disjoint Lands TEST_METHOD(TwoDisjointLands) { vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes; boxes.reserve(2); // prepare input boxes boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(3.0, 3.0, 6.0, 5.0)); // make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, boxes.size()); // two disjoint lands Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands()); } // Two Adjacient Lands TEST_METHOD(TwoAdjacientLands) { vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes; boxes.reserve(2); // prepare input boxes boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.5, 1.5, 6.0, 6.0)); // make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, boxes.size()); // two adjacient lands Assert::AreEqual<int>(1, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands()); } // Three Nested Boxes TEST_METHOD(ThreeNestedBoxes) { vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes; boxes.reserve(3); // prepare input boxes boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(15, 15, 85, 85)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(10, 10, 90, 90)); boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(0, 0, 100, 100)); // make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes Assert::AreEqual<int>(3, boxes.size()); // two adjacient lands Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands()); } }; } |
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CppUnitTest.h"
#include "../LandAndSea/box.h"
#include <vector>
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19886397/how-to-solve-the-error-lnk2019-unresolved-external-symbol-function
#include "../LandAndSea/landsolver.cpp"
using namespace Microsoft::VisualStudio::CppUnitTestFramework;
using namespace std;
namespace LandAndSeaTests
{
TEST_CLASS(LandSolverTests)
{
public:
// TestCase Given in the PDF
TEST_METHOD(ExampleTestCases)
{
vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes;
boxes.reserve(14);
// prepare input boxes
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.0, 1.0, 10.0, 6.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.5, 1.5, 6.0, 5.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(2.0, 2.0, 3.0, 3.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(2.0, 3.5, 3.0, 4.5));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(3.5, 2.0, 5.5, 4.5));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(4.0, 3.5, 5.0, 4.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(4.0, 2.5, 5.0, 3.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(7.0, 3.0, 9.5, 5.5));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(7.5, 4.0, 8.0, 5.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(8.5, 3.5, 9.0, 4.5));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(3.0, 7.0, 8.0, 10.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(5.0, 7.5, 7.5, 9.5));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(5.5, 8.0, 6.0, 9.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(6.5, 8.0, 7.0, 9.0));
// make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes
Assert::AreEqual<int>(14, boxes.size());
// now it should ouput 9
Assert::AreEqual<int>(9, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands());
}
// Two Disjoint Lands
TEST_METHOD(TwoDisjointLands)
{
vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes;
boxes.reserve(2);
// prepare input boxes
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(3.0, 3.0, 6.0, 5.0));
// make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes
Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, boxes.size());
// two disjoint lands
Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands());
}
// Two Adjacient Lands
TEST_METHOD(TwoAdjacientLands)
{
vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes;
boxes.reserve(2);
// prepare input boxes
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(1.5, 1.5, 6.0, 6.0));
// make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes
Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, boxes.size());
// two adjacient lands
Assert::AreEqual<int>(1, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands());
}
// Three Nested Boxes
TEST_METHOD(ThreeNestedBoxes)
{
vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes;
boxes.reserve(3);
// prepare input boxes
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(15, 15, 85, 85));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(10, 10, 90, 90));
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(0, 0, 100, 100));
// make sure we don't acidentally adding or deleting boxes
Assert::AreEqual<int>(3, boxes.size());
// two adjacient lands
Assert::AreEqual<int>(2, LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands());
}
};
}Box Class
A Box is defined by two coordinates (lower-left and upper-right). A Box is a region. We can define this using struct or vector of points.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 | #pragma once #include <exception> namespace LandAndSea { struct Point { double X, Y; }; class Box { public: // constructor with two corners of Point type Box(const Point &_lowerleft, const Point &_upperright): Box(_lowerleft.X, _lowerleft.Y, _upperright.X, _upperright.Y) { } // overload constructor lower left = (x1, y1), upper right = (x2, y2) Box(const double &x1, const double &y1, const double &x2, const double &y2) { lowerleft.X = x1; lowerleft.Y = y1; upperright.X = x2; upperright.Y = y2; if (!IsValid()) { throw std::exception("Invalid Box Values"); } } // check if box is disjoint with another box inline bool IsDisjoint(const Box &aBox) const { return !IsAdjacent(aBox); } // check if box is inside another box inline bool IsInside(const Box &aBox) const { return lowerleft.X > aBox.lowerleft.X && lowerleft.Y > aBox.lowerleft.Y && upperright.X < aBox.upperright.X && upperright.Y < aBox.upperright.Y; } // check if box A, B and C are inside each other A - innermost box inline bool IsInside(const Box &boxB, const Box &boxC) { return IsInside(boxB) && IsInside(boxC) && boxB.IsInside(boxC); } // check if box overlap or touch another box inline bool IsAdjacent(const Box &aBox) const { return !( (aBox.upperright.X < lowerleft.X) || (aBox.lowerleft.X > upperright.X) || (aBox.upperright.Y < lowerleft.Y) || (aBox.lowerleft.Y > upperright.Y) ); } private: Point lowerleft; Point upperright; // make sure lowerleft is smaller than upperright inline bool IsValid() { return lowerleft.X < upperright.X && lowerleft.Y < upperright.Y; } }; } |
#pragma once
#include <exception>
namespace LandAndSea {
struct Point
{
double X, Y;
};
class Box
{
public:
// constructor with two corners of Point type
Box(const Point &_lowerleft, const Point &_upperright): Box(_lowerleft.X, _lowerleft.Y, _upperright.X, _upperright.Y) { }
// overload constructor lower left = (x1, y1), upper right = (x2, y2)
Box(const double &x1, const double &y1, const double &x2, const double &y2) {
lowerleft.X = x1;
lowerleft.Y = y1;
upperright.X = x2;
upperright.Y = y2;
if (!IsValid())
{
throw std::exception("Invalid Box Values");
}
}
// check if box is disjoint with another box
inline bool IsDisjoint(const Box &aBox) const
{
return !IsAdjacent(aBox);
}
// check if box is inside another box
inline bool IsInside(const Box &aBox) const
{
return
lowerleft.X > aBox.lowerleft.X &&
lowerleft.Y > aBox.lowerleft.Y &&
upperright.X < aBox.upperright.X &&
upperright.Y < aBox.upperright.Y;
}
// check if box A, B and C are inside each other A - innermost box
inline bool IsInside(const Box &boxB, const Box &boxC)
{
return
IsInside(boxB) &&
IsInside(boxC) &&
boxB.IsInside(boxC);
}
// check if box overlap or touch another box
inline bool IsAdjacent(const Box &aBox) const
{
return !(
(aBox.upperright.X < lowerleft.X) ||
(aBox.lowerleft.X > upperright.X) ||
(aBox.upperright.Y < lowerleft.Y) ||
(aBox.lowerleft.Y > upperright.Y)
);
}
private:
Point lowerleft;
Point upperright;
// make sure lowerleft is smaller than upperright
inline bool IsValid()
{
return lowerleft.X < upperright.X && lowerleft.Y < upperright.Y;
}
};
}Let’s test this a little bit to make sure the basic functionalities work:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 | #include "stdafx.h" #include "CppUnitTest.h" #include "../LandAndSea/box.h" using namespace Microsoft::VisualStudio::CppUnitTestFramework; namespace LandAndSeaTests { TEST_CLASS(BoxTests) { public: // Tests for Two Overlapped Boxes TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsOverLap) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(5, 5, 100, 100); Assert::IsTrue(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox)); Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); } // Tests for Two Disjoint Boxes TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsDisjoint) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(100, 100, 200, 200); Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox)); Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); } // Tests for Touched Boxes TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesTouched) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20); Assert::IsTrue(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox)); Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); } // Tests for One box is entirely in another box TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesOneInAnother) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 100, 100); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20); Assert::IsTrue(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox)); Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox)); } // Tests for Two Disjoint Boxes Inside Test TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsDisjointInside) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(100, 100, 200, 200); Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox)); } // Tests for One box is entirely in another box TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesOneInAnotherInside) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 100, 100); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20); Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox)); Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox)); } // Tests for Touched Boxes Inside Tests TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesTouchedInside) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20); Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox)); } // Tests for Two Overlapped Boxes Inside Tests TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsOverLapInside) { LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10); LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(5, 5, 100, 100); Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox)); Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox)); } // Tests for Three Boxes TEST_METHOD(ThreeBoxesInside) { LandAndSea::Box boxC(0, 0, 100, 100); LandAndSea::Box boxB(5, 5, 95, 95); LandAndSea::Box boxA(15, 15, 85, 85); Assert::IsTrue(boxA.IsInside(boxB, boxC)); } }; } |
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CppUnitTest.h"
#include "../LandAndSea/box.h"
using namespace Microsoft::VisualStudio::CppUnitTestFramework;
namespace LandAndSeaTests
{
TEST_CLASS(BoxTests)
{
public:
// Tests for Two Overlapped Boxes
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsOverLap)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(5, 5, 100, 100);
Assert::IsTrue(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox));
Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
}
// Tests for Two Disjoint Boxes
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsDisjoint)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(100, 100, 200, 200);
Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox));
Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
}
// Tests for Touched Boxes
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesTouched)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20);
Assert::IsTrue(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox));
Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
}
// Tests for One box is entirely in another box
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesOneInAnother)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 100, 100);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20);
Assert::IsTrue(aBox.IsAdjacent(anotherBox));
Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsAdjacent(aBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsDisjoint(aBox));
}
// Tests for Two Disjoint Boxes Inside Test
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsDisjointInside)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(100, 100, 200, 200);
Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox));
}
// Tests for One box is entirely in another box
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesOneInAnotherInside)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 100, 100);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20);
Assert::IsTrue(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox));
Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox));
}
// Tests for Touched Boxes Inside Tests
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxesTouchedInside)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(10, 10, 20, 20);
Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox));
}
// Tests for Two Overlapped Boxes Inside Tests
TEST_METHOD(TwoBoxsOverLapInside)
{
LandAndSea::Box aBox(0, 0, 10, 10);
LandAndSea::Box anotherBox(5, 5, 100, 100);
Assert::IsFalse(aBox.IsInside(anotherBox));
Assert::IsFalse(anotherBox.IsInside(aBox));
}
// Tests for Three Boxes
TEST_METHOD(ThreeBoxesInside)
{
LandAndSea::Box boxC(0, 0, 100, 100);
LandAndSea::Box boxB(5, 5, 95, 95);
LandAndSea::Box boxA(15, 15, 85, 85);
Assert::IsTrue(boxA.IsInside(boxB, boxC));
}
};
}Land And Sea Solver Algorithm Class
C++ Header file to define the class. I was rejected because I used the “new” (which is like old-fashion C style) rather than using the modern C++ STL vector or the smart pointers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | #pragma once #include <vector> #include "box.h" namespace LandAndSea { // Type Land or Sea enum LandType { Land = 0, Sea = 1 }; class LandSolver { public: LandSolver() {} LandSolver(const std::vector<Box> &_boxes) : boxes(_boxes) { computeMap(); } ~LandSolver() { // free 2-dimensional array const int sz = boxes.size(); for (auto i = 0; i < sz; ++ i) { delete aMap[i]; } delete[] aMap; } // Returns the number of Land int GetNumberOfLands(); private: std::vector<Box> boxes; // contains pre-computed map to test if boxes[i] and boxes[j] are adjacient bool **aMap; // TODO: should replace this with vector void computeMap(); }; } |
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include "box.h"
namespace LandAndSea {
// Type Land or Sea
enum LandType {
Land = 0,
Sea = 1
};
class LandSolver
{
public:
LandSolver() {}
LandSolver(const std::vector<Box> &_boxes) : boxes(_boxes)
{
computeMap();
}
~LandSolver()
{
// free 2-dimensional array
const int sz = boxes.size();
for (auto i = 0; i < sz; ++ i)
{
delete aMap[i];
}
delete[] aMap;
}
// Returns the number of Land
int GetNumberOfLands();
private:
std::vector<Box> boxes;
// contains pre-computed map to test if boxes[i] and boxes[j] are adjacient
bool **aMap; // TODO: should replace this with vector
void computeMap();
};
}The implementation of the class – the Breadth First Search Algorithm (BFS)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 | #include "landsolver.h" #include <queue> #include <functional> using namespace LandAndSea; using namespace std; // compute aMap - lookup table to tell if a box is adjacient to another. // time O(n^3), space O(n^2) void LandSolver::computeMap() { const int sz = boxes.size(); aMap = new bool*[sz]; for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++ i) { aMap[i] = new bool[sz]; // box[i] is adjacient to itself aMap[i][i] = true; } for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++ i) { for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) { // two boxes are not overlapping, touching or containing if (boxes[i].IsDisjoint(boxes[j])) { aMap[i][j] = false; aMap[j][i] = false; continue; } // one is inside another, but we need to check if another is between if (boxes[i].IsInside(boxes[j]) || boxes[j].IsInside(boxes[i])) { bool ok = true; for (int k = 0; k < sz; ++ k) { if (k != i && k != j) { // i in j, i and j are NOT adjacient if k is between // j in i, i and j are NOT adjacient if k is between if (boxes[i].IsInside(boxes[k], boxes[j]) || boxes[j].IsInside(boxes[k], boxes[i])) { ok = false; break; } } } aMap[i][j] = ok; aMap[j][i] = ok; } else // touching or overlapping { aMap[i][j] = true; aMap[j][i] = true; } } } } // using BFS to get the maximum lands int LandSolver::GetNumberOfLands() { int numOfBoxes = boxes.size(); int maxland = 0; // BFS with Queue with pair box index, land type and the current maxland deque<pair<int, pair<vector<LandType>, int>>> Queue; // insert the first box index with land = true Queue.push_back(make_pair(0, make_pair(vector<LandType>(1, Land), 1))); // insert the first box index with sea = true Queue.push_back(make_pair(0, make_pair(vector<LandType>(1, Sea), 0))); while (Queue.size() > 0) { auto cur = Queue.front(); Queue.pop_front(); auto index = cur.first; auto landtype = cur.second.first; auto curMax = cur.second.second; // we have iterated all boxes if (index == numOfBoxes - 1) { maxland = max(maxland, curMax); } else { const auto list = boxes; auto boxmap = aMap; // check if we can place LandType given the existing landtypes const std::function<bool(vector<LandType>, int, LandType)> checkValid = [list, boxmap](vector<LandType> types, int newBoxIndex, LandType type) { for (size_t i = 0; i < types.size(); ++i) { // adjacent regions must not share the same classification. if (boxmap[i][newBoxIndex] && types[i] == type) { return false; } } return true; }; auto newBoxIndex = index + 1; if (checkValid(landtype, newBoxIndex, Land)) { // insert the next box index with land = true auto landtype1 = landtype; landtype1.push_back(Land); Queue.push_back(make_pair(newBoxIndex, make_pair(landtype1, curMax + 1))); } if (checkValid(landtype, newBoxIndex, Sea)) { // insert the next box index with sea = true auto landtype2 = landtype; landtype2.push_back(Sea); Queue.push_back(make_pair(newBoxIndex, make_pair(landtype2, curMax + 0))); } } } return maxland; } |
#include "landsolver.h"
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
using namespace LandAndSea;
using namespace std;
// compute aMap - lookup table to tell if a box is adjacient to another.
// time O(n^3), space O(n^2)
void LandSolver::computeMap()
{
const int sz = boxes.size();
aMap = new bool*[sz];
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++ i)
{
aMap[i] = new bool[sz];
// box[i] is adjacient to itself
aMap[i][i] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++ i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
{
// two boxes are not overlapping, touching or containing
if (boxes[i].IsDisjoint(boxes[j]))
{
aMap[i][j] = false;
aMap[j][i] = false;
continue;
}
// one is inside another, but we need to check if another is between
if (boxes[i].IsInside(boxes[j]) || boxes[j].IsInside(boxes[i]))
{
bool ok = true;
for (int k = 0; k < sz; ++ k)
{
if (k != i && k != j)
{
// i in j, i and j are NOT adjacient if k is between
// j in i, i and j are NOT adjacient if k is between
if (boxes[i].IsInside(boxes[k], boxes[j]) || boxes[j].IsInside(boxes[k], boxes[i]))
{
ok = false;
break;
}
}
}
aMap[i][j] = ok;
aMap[j][i] = ok;
}
else // touching or overlapping
{
aMap[i][j] = true;
aMap[j][i] = true;
}
}
}
}
// using BFS to get the maximum lands
int LandSolver::GetNumberOfLands()
{
int numOfBoxes = boxes.size();
int maxland = 0;
// BFS with Queue with pair box index, land type and the current maxland
deque<pair<int, pair<vector<LandType>, int>>> Queue;
// insert the first box index with land = true
Queue.push_back(make_pair(0, make_pair(vector<LandType>(1, Land), 1)));
// insert the first box index with sea = true
Queue.push_back(make_pair(0, make_pair(vector<LandType>(1, Sea), 0)));
while (Queue.size() > 0)
{
auto cur = Queue.front();
Queue.pop_front();
auto index = cur.first;
auto landtype = cur.second.first;
auto curMax = cur.second.second;
// we have iterated all boxes
if (index == numOfBoxes - 1)
{
maxland = max(maxland, curMax);
}
else
{
const auto list = boxes;
auto boxmap = aMap;
// check if we can place LandType given the existing landtypes
const std::function<bool(vector<LandType>, int, LandType)> checkValid = [list, boxmap](vector<LandType> types, int newBoxIndex, LandType type)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < types.size(); ++i)
{
// adjacent regions must not share the same classification.
if (boxmap[i][newBoxIndex] && types[i] == type)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
auto newBoxIndex = index + 1;
if (checkValid(landtype, newBoxIndex, Land))
{
// insert the next box index with land = true
auto landtype1 = landtype;
landtype1.push_back(Land);
Queue.push_back(make_pair(newBoxIndex, make_pair(landtype1, curMax + 1)));
}
if (checkValid(landtype, newBoxIndex, Sea))
{
// insert the next box index with sea = true
auto landtype2 = landtype;
landtype2.push_back(Sea);
Queue.push_back(make_pair(newBoxIndex, make_pair(landtype2, curMax + 0)));
}
}
}
return maxland;
}The main entry of the program dealing with the input/output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | #include <iostream> #include "box.h" #include <vector> #include "landsolver.h" using namespace std; int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes; for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++ i) { double a, b, c, d; // four corners of a box. cin >> a >> b >> c >> d; boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(a, b, c, d)); } cout << LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands() << endl; #ifdef _DEBUG cin >> n; #endif return 0; } |
#include <iostream>
#include "box.h"
#include <vector>
#include "landsolver.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<LandAndSea::Box> boxes;
for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
double a, b, c, d;
// four corners of a box.
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
boxes.push_back(LandAndSea::Box(a, b, c, d));
}
cout << LandAndSea::LandSolver(boxes).GetNumberOfLands() << endl;
#ifdef _DEBUG
cin >> n;
#endif
return 0;
}–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog)
loading...
Last Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Algorithms to Find the Cycle of a Linked List
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Introduction to Heap and Priority Queue