Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
You are given a list of bombs. The range of a bomb is defined as the area where its effect can be felt. This area is in the shape of a circle with the center as the location of the bomb.
The bombs are represented by a 0-indexed 2D integer array bombs where bombs[i] = [xi, yi, ri]. xi and yi denote the X-coordinate and Y-coordinate of the location of the ith bomb, whereas ri denotes the radius of its range.
You may choose to detonate a single bomb. When a bomb is detonated, it will detonate all bombs that lie in its range. These bombs will further detonate the bombs that lie in their ranges.
Given the list of bombs, return the maximum number of bombs that can be detonated if you are allowed to detonate only one bomb.
Example 1:
Input: bombs = [[2,1,3],[6,1,4]]
Output: 2
Explanation:
The above figure shows the positions and ranges of the 2 bombs.
If we detonate the left bomb, the right bomb will not be affected.
But if we detonate the right bomb, both bombs will be detonated.
So the maximum bombs that can be detonated is max(1, 2) = 2.Example 2:
Input: bombs = [[1,1,5],[10,10,5]]
Output: 1
Explanation:
Detonating either bomb will not detonate the other bomb, so the maximum number of bombs that can be detonated is 1.Example 3:
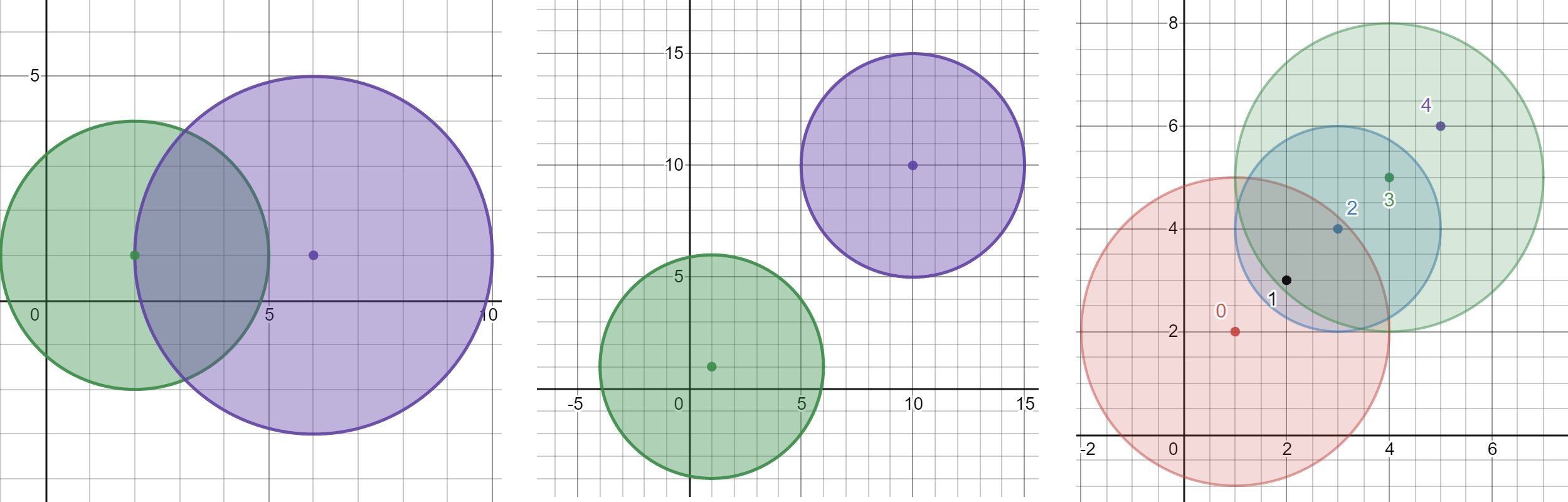
Input: bombs = [[1,2,3],[2,3,1],[3,4,2],[4,5,3],[5,6,4]]
Output: 5
Explanation:
The best bomb to detonate is bomb 0 because:
– Bomb 0 detonates bombs 1 and 2. The red circle denotes the range of bomb 0.
– Bomb 2 detonates bomb 3. The blue circle denotes the range of bomb 2.
– Bomb 3 detonates bomb 4. The green circle denotes the range of bomb 3.
Thus all 5 bombs are detonated.Constraints:
1 <= bombs.length <= 100
bombs[i].length == 3
1 <= xi, yi, ri <= 10^5
Breadth First Search Algorithm to Compute the Maximum Number of Connected Components in a Directed Graph (Detonate the Maximum Bombs)
In last talk (Teaching Kids Programming – Max Number of Connected Components in a Directed Graph (Detonate the Maximum Bombs) via Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm), we have used the Depth First Search (DFS) in the manner of Recursion to solve this puzzle. We can also use the Breadth First Search (BFS) to traversal the Directed Graph. The other parts are the same: constructing a directed graph from a list of the coordinates and their corresponding radius; checking if bomb B can be detonated if we ignite bomb A (if there is a directed edge from vertex A to vertex B).
The time complexity is O(N^3) – which is the same to DFS approach. We need to try BFS n times, and each BFS takes O(N^2) time. Same space complexity e.g. O(N^2) for the usage of Adjacency List to store the Directed Graph.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | class Solution: def maximumDetonation(self, bombs: List[List[int]]) -> int: def f(a, b): x1, y1, r1 = a x2, y2, _ = b return (x1-x2)**2 + (y1-y2) **2 <= r1**2 G = defaultdict(list) n = len(bombs) for i in range(n): for j in range(n): if i != j and f(bombs[i], bombs[j]): G[i].append(j) def bfs(x): q = deque([x]) seen = set([x]) while q: c = q.popleft() for x in G[c]: if x not in seen: seen.add(x) q.append(x) return len(seen) return max((bfs(i) for i in range(n)), default=0) |
class Solution:
def maximumDetonation(self, bombs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def f(a, b):
x1, y1, r1 = a
x2, y2, _ = b
return (x1-x2)**2 + (y1-y2) **2 <= r1**2
G = defaultdict(list)
n = len(bombs)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if i != j and f(bombs[i], bombs[j]):
G[i].append(j)
def bfs(x):
q = deque([x])
seen = set([x])
while q:
c = q.popleft()
for x in G[c]:
if x not in seen:
seen.add(x)
q.append(x)
return len(seen)
return max((bfs(i) for i in range(n)), default=0)The return value of the BFS is the number of the connected vertices aka the bombs that can be detonated at the same time)
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Max Number of Connected Components in a Directed Graph (Detonate the Maximum Bombs) via Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
Next Post: How to Get the Original File Name, Title, File Size, Video Format (mp4 or mov) and Length for Videos using Youtube Data API?