Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
Given two binary trees original and cloned and given a reference to a node target in the original tree. The cloned tree is a copy of the original tree. Return a reference to the same node in the cloned tree. Note that you are not allowed to change any of the two trees or the target node and the answer must be a reference to a node in the cloned tree.
Example 1:
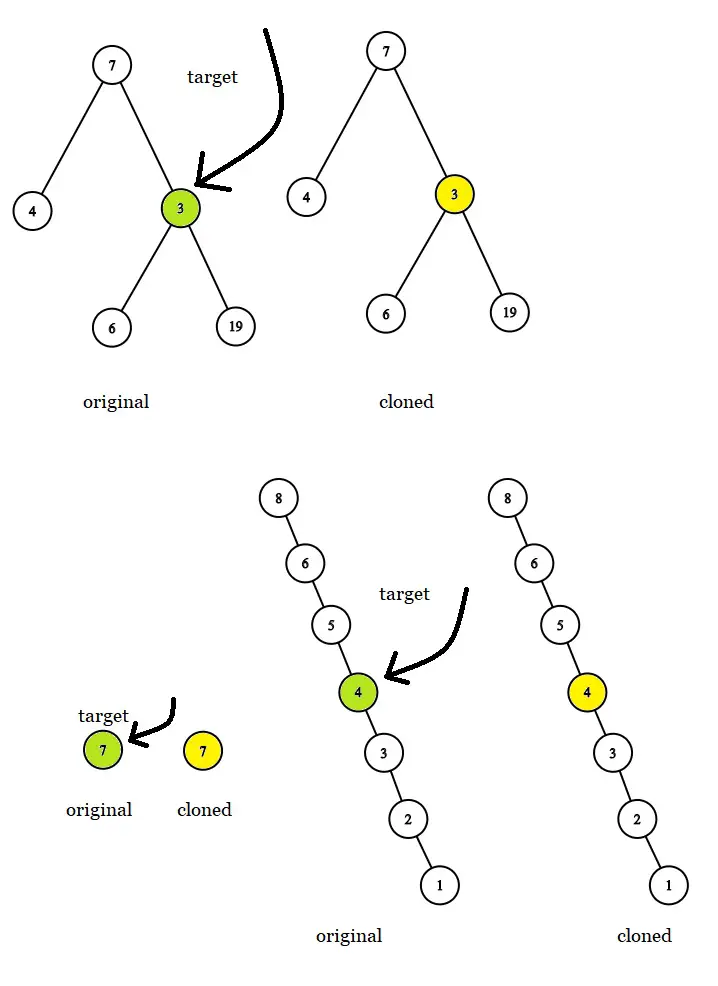
Input: tree = [7,4,3,null,null,6,19], target = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: In all examples the original and cloned trees are shown. The target node is a green node from the original tree. The answer is the yellow node from the cloned tree.Example 2:
Input: tree = [7], target = 7
Output: 7Example 3:
Input: tree = [8,null,6,null,5,null,4,null,3,null,2,null,1], target = 4
Output: 4Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104].
The values of the nodes of the tree are unique.
target node is a node from the original tree and is not null.Follow up: Could you solve the problem if repeated values on the tree are allowed?
Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree via Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
We can traverse the binary tree and its clone synchronously (at the same pace). We can Depth First Search, and the easiest way would be to use Recursion. The order of the traversal (Preorder, Inorder, Postorder) does not matter as long as all the nodes are visited.
With Recursive DFS, we can implement it as the following where the DFS function returns the node or None if not found.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | class Solution: def getTargetCopy(self, a: TreeNode, b: TreeNode, target: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: def dfs(a, b, t): if not a: return None if a.val == t.val: return b x = dfs(a.left, b.left, t) if x: return x return dfs(a.right, b.right, t) return dfs(a, b, target) |
class Solution:
def getTargetCopy(self, a: TreeNode, b: TreeNode, target: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
def dfs(a, b, t):
if not a:
return None
if a.val == t.val:
return b
x = dfs(a.left, b.left, t)
if x:
return x
return dfs(a.right, b.right, t)
return dfs(a, b, target)Also, we can set self.ans (Solution.ans) once we found the corresponding node.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class Solution: def getTargetCopy(self, a: TreeNode, b: TreeNode, target: TreeNode) -> TreeNode: self.ans = None def dfs(a, b, t): if not a: return if a is t: self.ans = b return dfs(a.left, b.left, t) if self.ans: return dfs(a.right, b.right, t) dfs(a, b, target) return self.ans |
class Solution:
def getTargetCopy(self, a: TreeNode, b: TreeNode, target: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
self.ans = None
def dfs(a, b, t):
if not a:
return
if a is t:
self.ans = b
return
dfs(a.left, b.left, t)
if self.ans:
return
dfs(a.right, b.right, t)
dfs(a, b, target)
return self.ansBoth algorithms have O(N) time complexity and O(N) space due to Recursion. The Recursion will stop once the node is found.
Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
- Teaching Kids Programming – Breadth First Search Algorithm to Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
- Teaching Kids Programming – Iterative Depth First Search Algorithm to Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
- Teaching Kids Programming – Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree via Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Breadth First Search Algorithm to Find the Sum of Deepest Leaves in a Binary Tree
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Iterative Depth First Search Algorithm to Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree