Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
Given two integers n and k, return all possible combinations of k numbers out of 1 … n. You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, k = 2
Output:
Example 2:
Input: n = 1, k = 1
Output: [[1]]
Compute the Combinations via Recursive Backtracking (Depth First Search)
There are 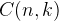 number of the combinations when you pick k items out of n. Therefore, the solution time complexity is
number of the combinations when you pick k items out of n. Therefore, the solution time complexity is 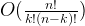 . We can backtracking with Depth First Search so that for each round, we can pick an item and DFS to next pick until we have k items.
. We can backtracking with Depth First Search so that for each round, we can pick an item and DFS to next pick until we have k items.
This is similar to Permutations where each result can have K! different sequences: Teaching Kids Programming – Recursive Permutation Algorithm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | class Solution: def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]: def dfs(left, cur): if len(cur) == k: # finish k items output.append(cur[:]) return for i in range(left, n + 1): cur.append(i) # pick i dfs(i + 1, cur) # pick next from i+1 cur.pop() # reset for next iteration output = [] dfs(1, []) return output |
class Solution:
def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(left, cur):
if len(cur) == k: # finish k items
output.append(cur[:])
return
for i in range(left, n + 1):
cur.append(i) # pick i
dfs(i + 1, cur) # pick next from i+1
cur.pop() # reset for next iteration
output = []
dfs(1, [])
return output Permutations and Combinations
- Using Bitmasking Algorithm to Compute the Combinations of an Array
- Teaching Kids Programming – Recursive Backtracking Algorithm to Compute the Combinations
- Teaching Kids Programming – Recursive Permutation Algorithm
- Teaching Kids Programming – Introduction to Permutation and Combination
- Teaching Kids Programming – Three Algorithms to Compute the Combination Number
- A Recursive Full Permutation Algorithm in Python
- The Permutation Iterator in Python
- GoLang: Full Permutation Command Line Tool
- The Permutation Algorithm for Arrays using Recursion
- Full Permutation Algorithm Implementation in BASH
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
GD Star Rating
loading...
623 wordsloading...
Last Post: Rolling Hash Algorithm to Find the Longest Prefix that Is a Suffix
Next Post: Algorithms to Compute the Interleaved Linked List