Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
In Python, we have following three ways to creating a hash table:
1 2 3 | a = {} a = dict() a = defaultdict(int) # value type is int |
a = {}
a = dict()
a = defaultdict(int) # value type is intThe first two are equivalent: when keys do not exist in the hash table, an exception will be thrown when you try to update/remove the key-value pair. The hash table created by third approach will return a default value for the type.
You can however, use the get method to specify a default value, for example:
1 | a.get("key", "default value") |
a.get("key", "default value")What is a hash function?
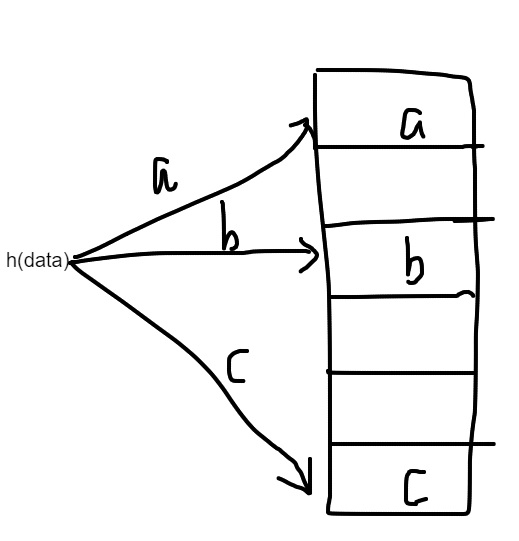
A hash function h(x) maps the data x (any length) into a fixed-size space. For example, it could be 32-bit integer, or 256-bit data e.g. SHA-256 cryptography hashing function. A hash function helps to make the following three operations regarding to a hash table practically fast O(1) constant time:
- Lookup a key
- Update a key-value pair
- Remove a key
The hash function is essentially important as all these operations require locating the address to store the item. A hash function is one-way so it is not possible to get the original item from a hash value. A hash function needs to have the following characteristics to have a performant hash table.
- Fast: If a hash key computation process is slow – we will lose the advantages of using a hash table.
- Less Collison: If a collison is likely to happen, the peformance of a hash table will be slow
- Avalanche Effect: a slight change in the input data need to result in totally different hash value – for better security so that the original data can not be deduced.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
loading...
Last Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Convert 1-D Array to 2D Matrix (Reshape Algorithm)
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Design a Hash Table